
Chou’s Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric, 6eĢ.

Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) with Strain Pattern ECG (Example 1).Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) ECG (Example 4).Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) ECG (Example 3).Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) ECG (Example 2).Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) ECG (Example 1).Intrinsicoid deflection in V5 or V6 > 50 ms = 1 point.ST and T wave changes opposite QRS with digoxin = 1 point.ST and T wave changes opposite QRS without digoxin = 3 points.Amplitude of R in V5 or V6 ≥ 30 mm = 3 points.Amplitude of S in V1 or V2 ≥ 30 mm = 3 points.Amplitude of largest R or S in limb leads ≥ 20 mm = 3 points.If the score is greater than 5, LVH is present with 83% to 97% specificity. Romhilt-Estes LVH Point Score System: If the score equals 4, LVH is present with 30% to 54% sensitivity. If the sum is greater than 35 mm, LVH is present.
Sr lad borderline ivcd plus#
Sokolow-Lyon Criteria: Add the S wave in V1 plus the R wave in V5 or V6. If the R wave is greater than 12 mm in amplitude, LVH is present. Modified Cornell Criteria: Examine the R wave in aVL. If the sum is greater than 28 millimeters in males or greater than 20 mm in females, LVH is present.
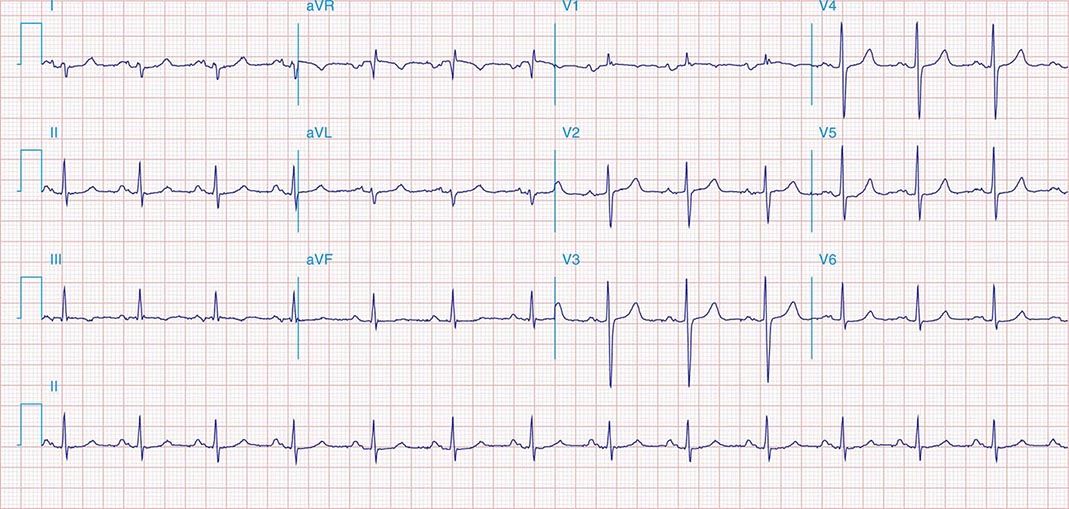
Through many studies, multiple criteria have been developed to diagnose LVH on an ECG they are listed below.Ĭornell criteria: Add the R wave in aVL and the S wave in V3. The typical pattern with LVH includes deviation of the ST segment in the opposite direction of the QRS complex (discordance), and a typical T wave inversion pattern is present, as seen in the image here:Įnlarge Left Ventricular Hypertrophy ECG Criteria
This is referred to as “LVH with strain” or “LVH with repolarization abnormality.”Īt times, these repolarization abnormalities can mimic ischemic ST changes, and distinguishing them from those during a myocardial infarction is important, though often difficult. This is referred to as “LVH with QRS widening.” Also, repolarization may be affected via similar mechanisms that can result in abnormal ST segments or T waves. Likewise, when the myocardium is abnormally thickened, and electrical activity takes longer to traverse throughout the whole heart, the duration of the QRS complex may be widened. When the myocardium is hypertrophied, there is a larger mass of myocardium for electrical activation to pass through thus the amplitude of the QRS complex, representing ventricular depolarization, is increased. Left ventricular hypertrophy can be diagnosed on ECG with good specificity. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) ECG Review


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
